Wastewater Treatment by MBBR Method
Wastewater treatment using the MBBR (Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor) method is a subset of extended aeration activated sludge treatment. It significantly reduces BOD and pollutants in both sanitary and industrial wastewater. The primary privilege between MBBR and conventional extended aeration activated sludge systems based in the use of biomass growth on the packing media in the treatment process, which enhances the removal of organic components by microorganisms. Below, we provide a comprehensive introduction to the MBBR method, including its treatment stages, advantages, disadvantages, and applications.
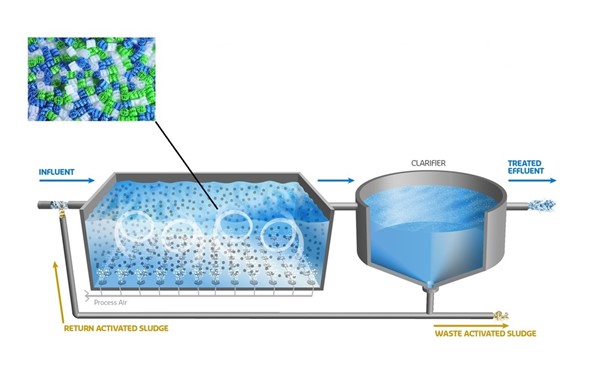
What is Wastewater Treatment by MBBR Method?
In the field of sanitary and industrial wastewater treatment, numerous challenges exist, among which the presence of high concentrations of organic matter and nitrates in effluents is one of the most significant. To mitigate the impact of these substances before they enter the environment, there are many solutions have been proposed with biological treatment being the primary approach. In biological treatment methods, the aim is to utilize aerobic and anaerobic microorganisms and bacteria to digest the organic matter and improve wastewater quality. MBBR is one of the methods developed for this purpose. Essentially, it is an extended aeration activated sludge wastewater treatment process that incorporates packing media for small biomass carriers. This system significantly reduces sludge production compared to conventional activated sludge systems which is a major advantage, and there will no need to return activated sludge to the aeration tank.
Packaging media or biomass carriers refer to small pieces, often made of polyethylene, that provide a surface for the growth and proliferation of microorganisms. By introducing these small carriers into the aeration tank, microorganisms attach to their surfaces. Essentially, the packaging media create additional surface area for microbial growth, enabling microorganisms to thrive and consume more organic matter. The consumption and breakdown of organic matter by bacteria attached to the biomass carriers lead to improved effluent quality and a reduction in BOD.

Steps of Wastewater Treatment Using the MBBR Method
Generally, wastewater treatment tanks or packages that utilize the MBBR method to improve effluent quality parameters consist of several key sections and steps, which include:
The first step in the MBBR treatment process is the removal of trashes from the wastewater, which do not significantly affect BOD, COD, or other wastewater quality parameters. This step reduces the pressure on treatment equipment in subsequent stages and improves the treatment efficiency. The process of separating trashes is carried out using manual screens or mechanical screens, the selection of which depends on the size (capacity) of the treatment plant.
Aeration Tank
One of the most critical and essential part of wastewater treatment using the MBBR method is the aeration tank, where extensive and deep aeration takes place. In this stage, small-sized biomass or packing media are introduced into the wastewater in large quantities, and aeration is performed using diffusers. The deep aeration enter a significant amount of oxygen is infused into the wastewater, ideally facilitating the growth of aerobic bacteria. It is also important to note that special nets are installed over the tanks to prevent the escape of suspended packing media.
Sludge Settling Unit
Aerobic bacteria in the wastewater gradually grow by consuming organic matter, adhere to each other, and will be get weigher. The significant weight of these mass causes them to sink and settle at the bottom of the sedimentation tank. In MBBR process of wastewater treatment, the produced sludge is not recirculated back into the aeration tank, meaning there is no return sludge. The accumulated sludge at the bottom of the tanks is collected and discharged, while the effluent with a very low percentage of organic matter exits the tank or treatment package.
Chemical Wastewater Treatment (Optional)
As the final step in this treatment method, chemical wastewater treatment can be implemented. In this stage, colloidal particles are aggregated and disinfected using equipment such as chlorination packages, coagulants.

Advantages of Wastewater Treatment with MBBR
- Use of packing media or biomass carriers enhances conditions for aerobic bacterial growth, ultimately increasing treatment efficiency and performance.
- Packing media significantly reduces sludge production, lowering the costs associated with collecting and disposing of accumulated sludge in settling tanks.
- Fluctuations and small shock loads in incoming wastewater do not destabilize the treatment process, ensuring consistent operation.
- This method maintains high pollutant removal efficiency across environments with varying pH levels and temperatures.
Applications of Wastewater Treatment Using the MBBR Method
Given the highly favorable impact of the MBBR method on reducing organic matter in wastewater, coupled with the low setup costs of required treatment plants, this method is applicable in numerous environments. Key applications include:
- Treatment of residential complex wastewater
- Industrial wastewater treatment
- Effluent treatment for refineries and power plants
- Treatment of hospital wastewater at low cost and in a short time
- Significant reduction of organic load in wastewater from detergent and pharmaceutical manufacturing plants
- Slaughterhouse wastewater treatment.
- Wastewater treatment for steel production plants
Wastewater treatment for paper manufacturing plants
